Infrastructure Automation Suite
Self-service automation reducing ops workload by 30 hours/week
Problem & Context
The Challenge
Routine infrastructure tasks (server health checks, database backups, log rotation, certificate renewals) consumed 30+ engineer hours/week and were prone to human error.
Context
Part of platform team responsible for maintaining 200+ Windows/Linux servers, 50+ databases, and various middleware. Manual operations were bottleneck and risk.
System Overview
Built automation framework with Python/PowerShell scripts, RESTful APIs for integration, MongoDB for state tracking, scheduled execution via cron/Task Scheduler, Slack notifications for failures, and self-service web portal for common tasks.
Architecture
Event-driven automation platform with script library, execution engine, state management, and notification system.
Visual Evidence
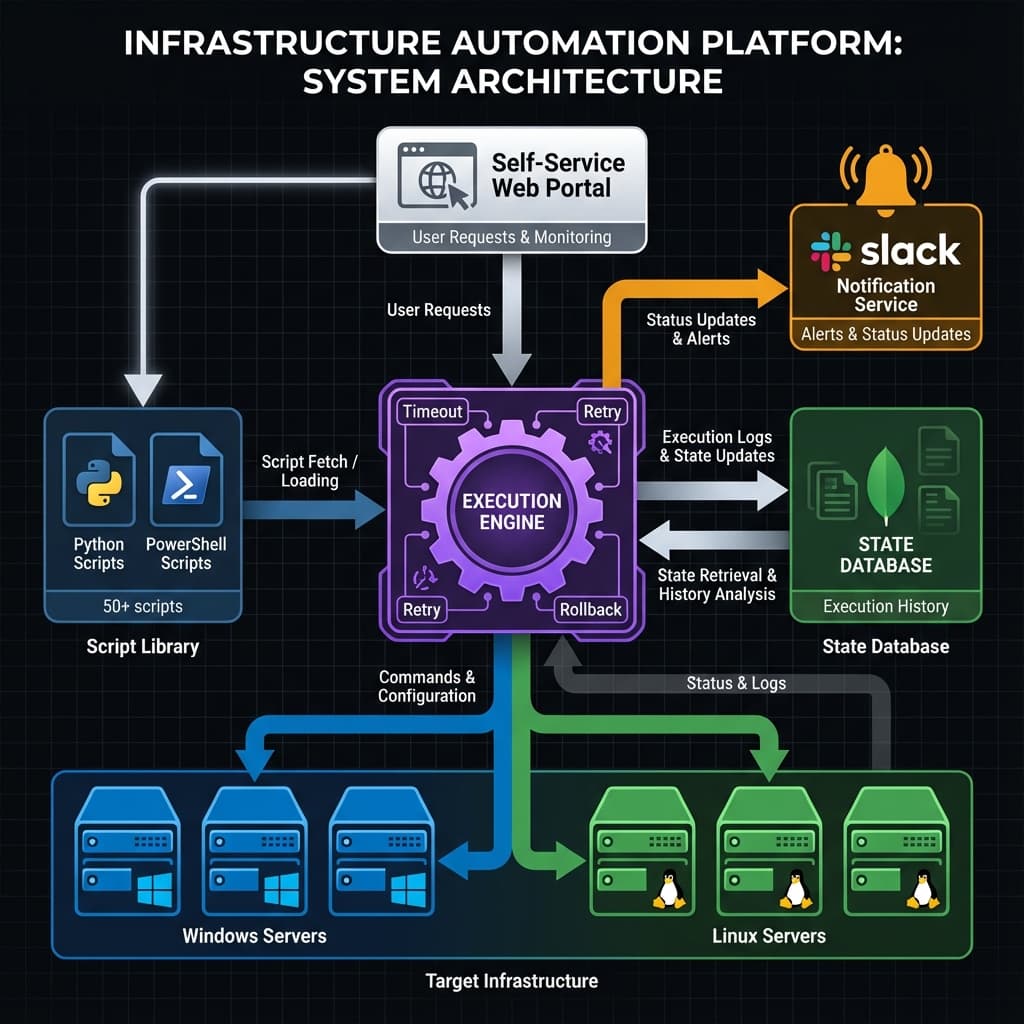
Infrastructure Automation Platform: Self-service portal, script library (Python/PowerShell), execution engine with rollback, state database, notification service, targeting Windows/Linux servers
Tech Stack
Key Engineering Decisions
Language Choice: Python vs PowerShell
Mixed Windows/Linux environment, different team skillsets
Python for cross-platform logic, PowerShell for Windows-specific tasks, with unified API layer
Maintained two languages but leveraged strengths of each
Idempotency Strategy
Scripts may run multiple times (retries, manual triggers)
Implemented state checking before every action, dry-run mode, and rollback capability
Added complexity but eliminated double-execution risks
Results & Impact
Engineer Time Saved
Manual Errors
Ops Tasks Automated
Incident Recovery Time
Failures & Learnings
Idempotency is non-negotiable for automation - design for retries from day 1
Logging/observability for scripts is as important as for applications
Self-service UIs drive adoption - CLI-only tools stay niche
Version control + code review for automation prevents catastrophic mistakes
Rollback/dry-run modes build trust in automation